- Human. The number of deaths has been quantified by more than 50 million, of which more than half were civilians, women and children. Poland was the country with the highest percentage of deaths (20 per 100 of the population), followed by the Soviet Union and Yugoslavia. Some of these dead were victims of the Nazi anti-Semitic policy, called Final Solution , and that the Jews remember as a Holocaust. After the quick conquest of Europe, the Germans thought to send all the Jews to the island of Madagascar. Between the years 1936 and 1939, more than 600000 German Jews emigrated, abandoning all their properties The large number of Jews residing in occupied Europe made it impossible to emigrate all of them, and the Germans confined them to concentration camps, some of which became extermination camps, such as those of Auschwitz, Treblinka and Sobibor.
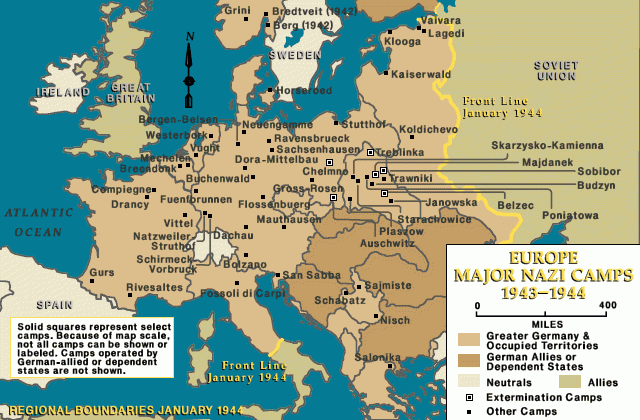
- From the end of 1939 until the beginning of 1945, nearly six million Jews were assassinated, as well as Romanies, Soviet prisoners of war, slavic people and communists.To punish these crimes, 20 Noviemhre 1945, 199 Nazi leaders and collaborators were tried in a special court in Nuremberg. When the war ended, more than 30 million of human beings were repatriated. They were displaced people from their homes by war: survivors of concentration camps, people expelled from some countries to others, workers forcibly transferred, collaborators who fled to other countries, Germans who remained in Poland, Ukraine and Romania because the Nazis had forced them to colonize these countries. The Allied authorities had to take care of these millions of people that the war left homeless.
- Economical. As a result of the battles and the bombardments, all the occupied cities of Europe were destroyed, as well as the ports, the railways, the roads and the fields of cultivation. The total cost of the war was about three trillion dollars. European countries lost its economical power and depended on the grants of the USA. The economic and supply problems in raw materials in European countries led the French politician Schuman to propose, in 1950, the creation of an organism for the exchange of coal and steel to facilitate the reconstruction of Europe: the Community Economic Coal and Steel (ECSC, CECA in Spanish).
- Political and ideological.
Europe definitely lost its hegemonic role in the world in favor of the United States. The European countries lost their colonies in Africa and Asia, most of the times, after bloody wars of liberation.
Monarchies disappeared in Italy, Yugoslavia, Bulgaria, Romania and Albania to make way for new republics.
The world was divided into two ideologically different blocks: the Communist, led by the Soviet Union, and the liberal-capitalist, championed by the United States. The USSR annexed the Baltic States and maintained under its influence the majority of the countries that were liberated by the Red Army: Poland, Bulgaria, Czechoslovakia, Hungary, Romania and East Germany. In these countries, democratic parties were abolished and the Soviet single-party model was imposed. - Territorial.
- The USSR recovered the territories it had lost in 1941.
- Bulgaria ceded Macedonia to Yugoslavia, and Thrace to Greece.
- Italy renounced all its colonies and returned the Dodecanese to Greece.
- Austria and Czechoslovakia regained their independence.
- Germany was divided into four zones of occupation, administered by the four Allied powers, of which two nations would emerge: the Federal Republic of Germany and the German Democratic Republic.
- Japan was forced to return the occupied territories to China, and the United States occupied Pacific islands.
- Korea was divided into two by the parallel 38° and under the Soviet and North American protection.
iiww
Consequences of the war
Obra publicada con Licencia Creative Commons Reconocimiento Compartir igual 4.0